HOW AMAZON RDS, AURORA, AND ELASTICACHE WORK TOGETHER FOR SCALABLE E-COMMERCE APPLICATIONS
A Story of Building Scalable E-Commerce on AWS
Imagine you are launching a new e-commerce platform. At first, traffic is light. Customers browse products, add items to their cart, and place orders. A single database server feels enough. But as your store grows, traffic spikes on Black Friday and suddenly… your database starts slowing down. Pages load slowly, carts fail to update, and checkout becomes unreliable.
This is where AWS managed database services come to the rescue.
Step 1: Amazon RDS – The Foundation
Amazon RDS (Relational Database Service) is the backbone. It allows you to run familiar engines like MySQL, PostgreSQL, or Oracle without worrying about manual setup, backups, or patching.
-
Multi-AZ Deployment → ensures high availability. If one AZ fails, AWS automatically fails over to another.
-
Read Replicas → scale your read traffic across replicas while keeping the main DB for writes.
💡 Example: Your checkout system uses the primary RDS instance, while your analytics dashboard queries a read replica, preventing reporting queries from slowing down customers.
Step 2: Amazon Aurora – Supercharged RDS
When growth accelerates, you may need more performance. That’s where Amazon Aurora comes in. Aurora is AWS’s cloud-native relational database that is 5x faster than MySQL and 3x faster than PostgreSQL.
-
It automatically replicates data across six copies in three AZs.
-
Storage scales up to 128TB automatically.
-
Aurora Replicas help you handle massive read traffic seamlessly.
💡 Example: During a holiday sale, Aurora automatically adjusts to heavy spikes, so your product pages never slow down.
Step 3: RDS Proxy – The Connection Manager
Your application servers (EC2, ECS, or Lambda) may open thousands of database connections at once. Databases struggle with this.
👉 RDS Proxy acts as a middle layer, pooling and managing connections. This reduces load on the database and improves failover times.
💡 Example: When 10,000 users log in at once, RDS Proxy ensures your database doesn’t get overwhelmed.
Step 4: Amazon ElastiCache – Lightning Fast Performance
Some queries don’t need to hit the database at all. Imagine the “Top 10 Trending Products” widget or storing a shopping cart session.
👉 With Amazon ElastiCache (Redis or Memcached), your app fetches data in microseconds instead of querying the DB.
-
Lazy loading → fetch data only when missing from cache.
-
Write-through caching → updates cache whenever DB updates.
-
TTL expiry → automatically removes stale data.
💡 Example: Netflix uses caching to display recommended movies instantly. Your e-commerce store can do the same with ElastiCache for products and sessions.
Step 5: MemoryDB for Redis – Caching with Durability
If you want caching that survives failures, Amazon MemoryDB for Redis adds durability and multi-AZ resilience. Perfect for financial apps or real-time leaderboards.
💡 Example: A trading app uses MemoryDB to store real-time stock prices without losing data during outages.
Bringing It All Together
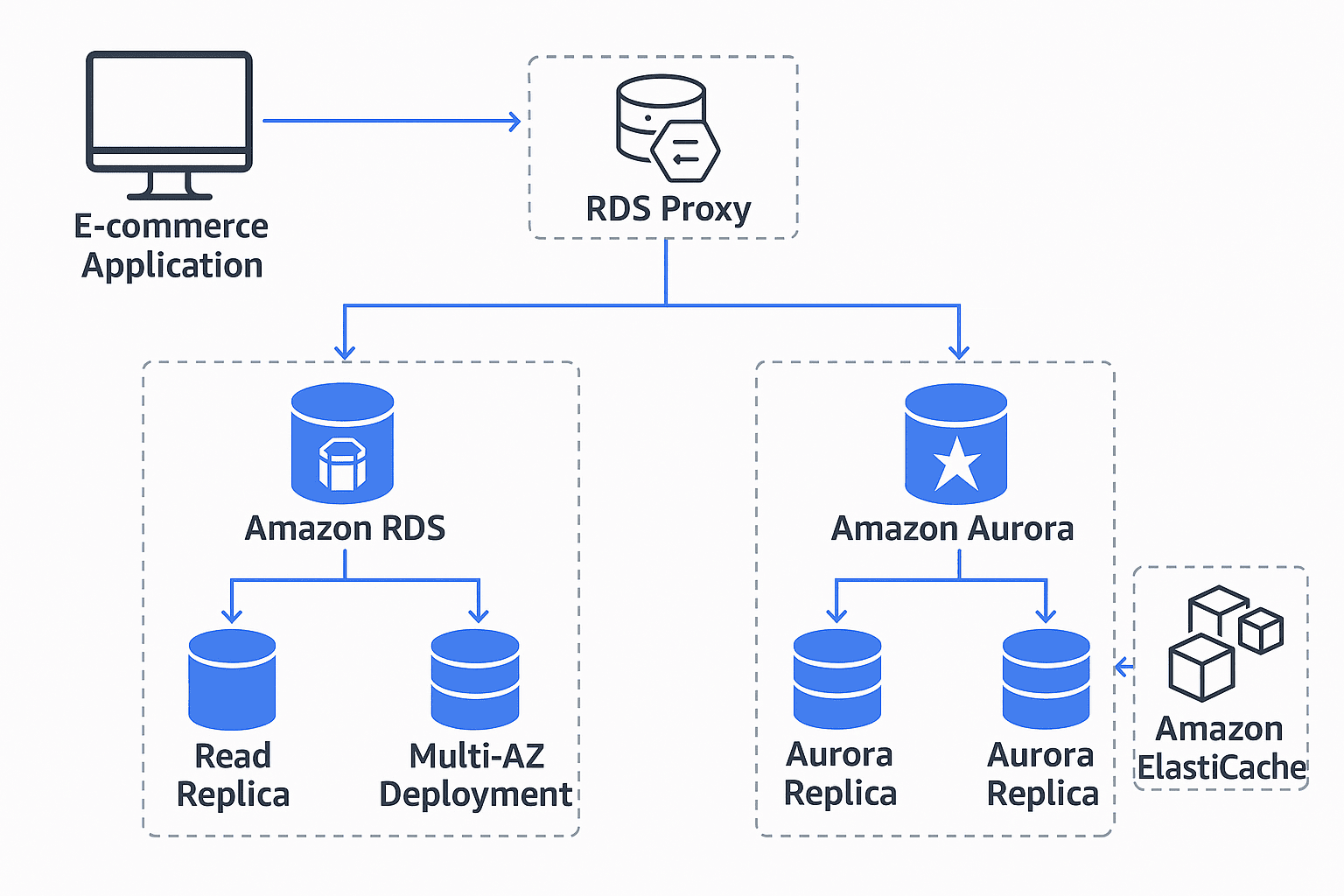
The diagram above illustrates how these AWS services work in harmony:
-
Users interact with your E-commerce Application.
-
Application servers connect to the database via RDS Proxy.
-
The backend uses RDS or Aurora for primary storage (Multi-AZ for HA, Read Replicas for scaling).
-
Frequently accessed data is cached in ElastiCache.
This architecture ensures your store remains:
-
Highly Available (Multi-AZ, Aurora)
-
Scalable (Read Replicas, Aurora Replicas)
-
Fast (ElastiCache, MemoryDB)
-
Secure (IAM auth, KMS encryption, private subnets)